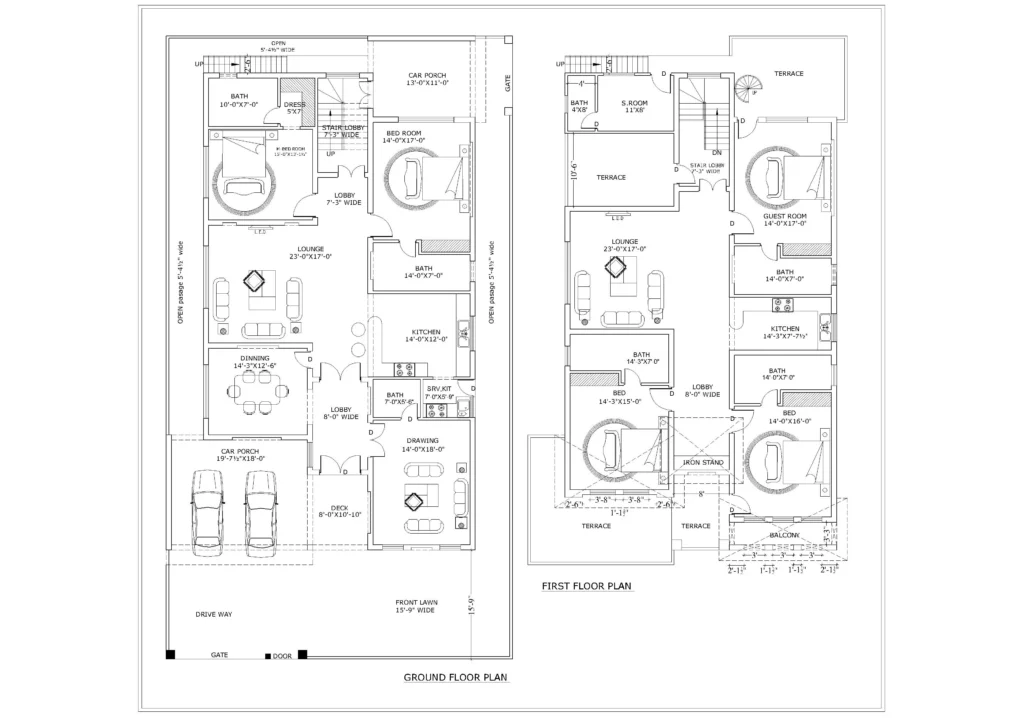
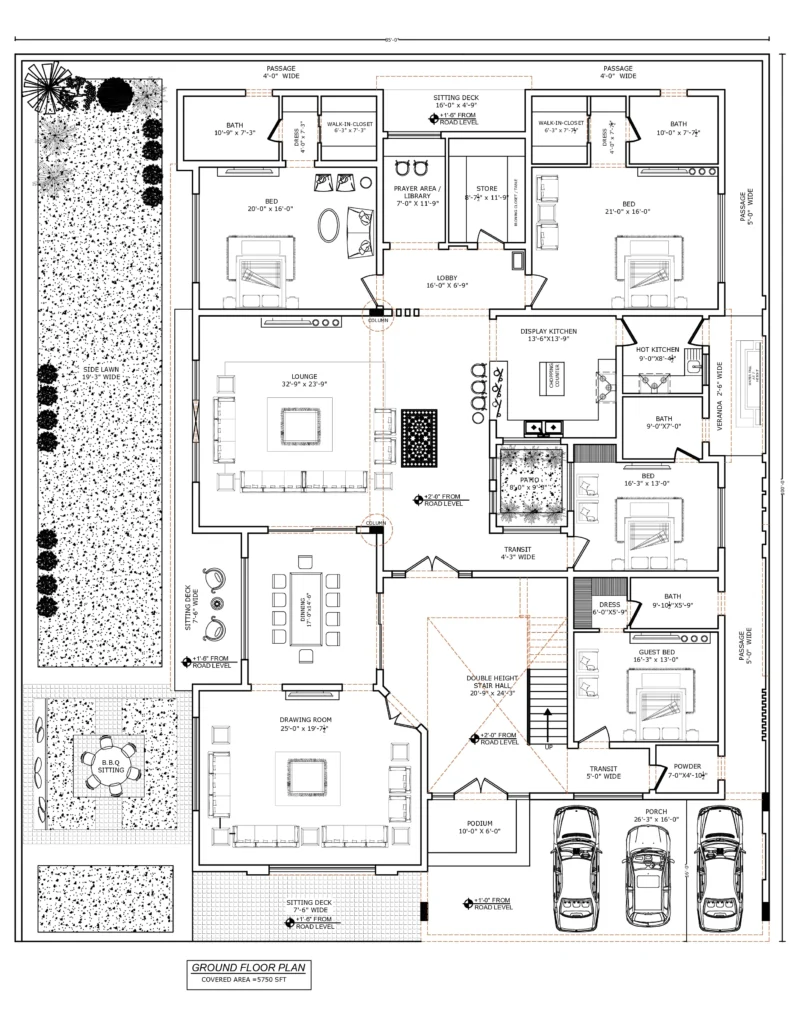
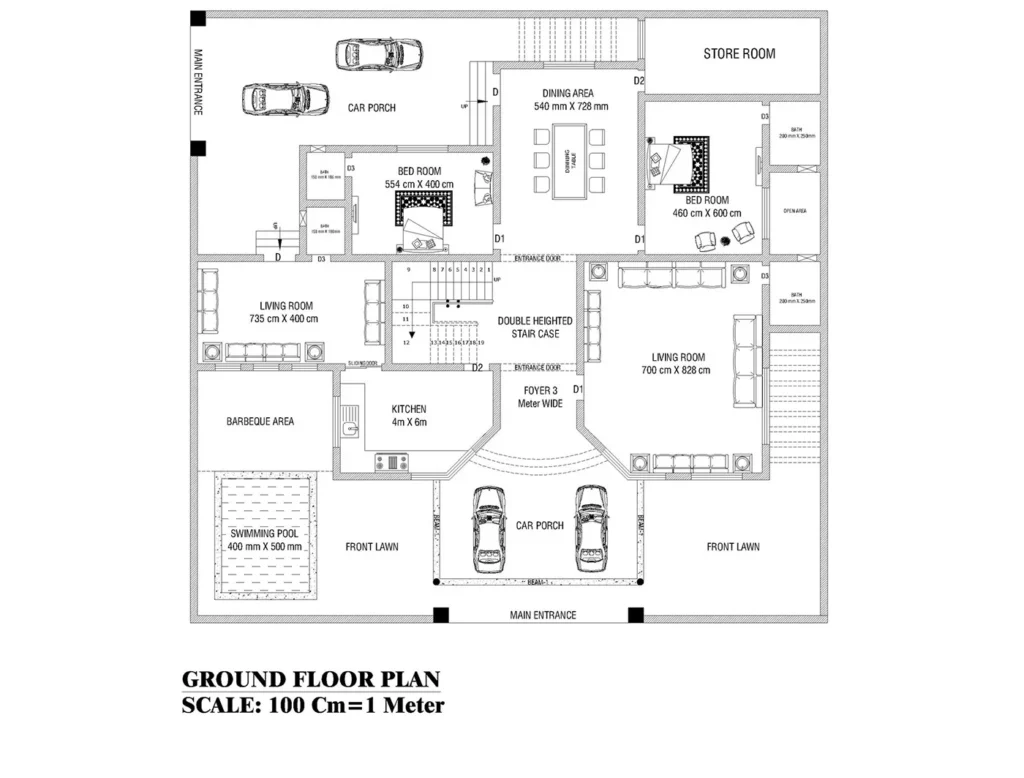
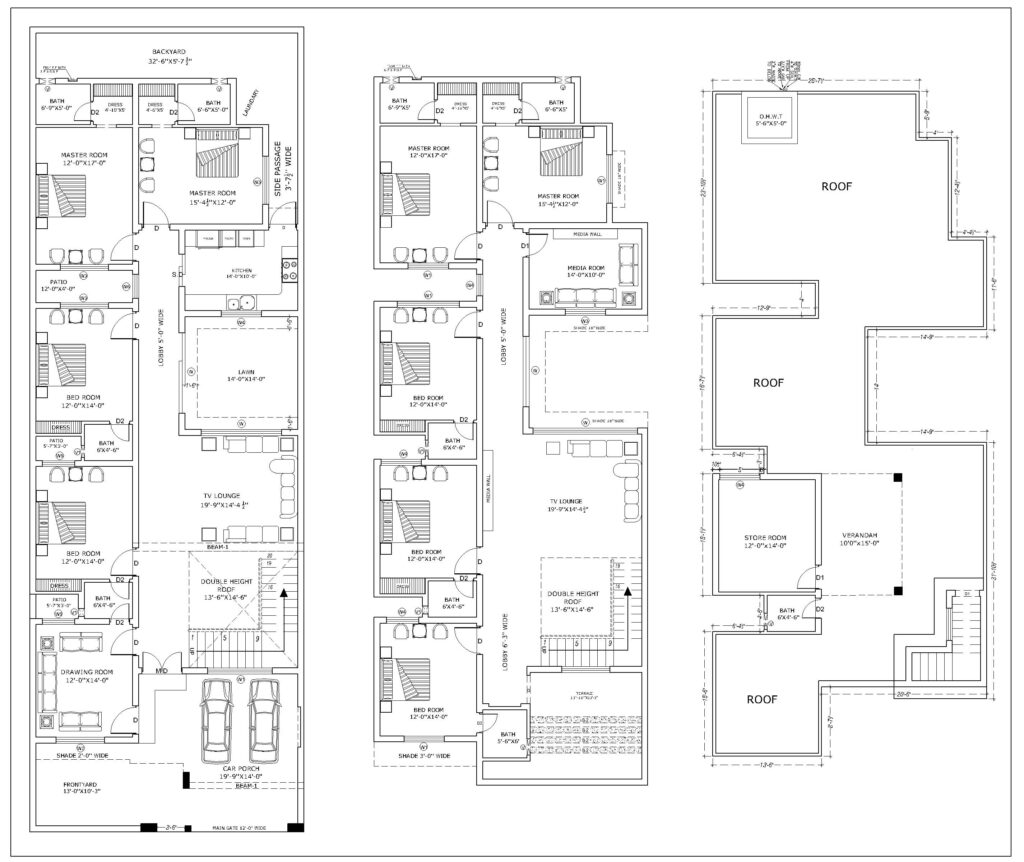
Building Plan:
A Building Plan is a detailed blueprint or set of drawings that outlines the layout, dimensions, and design features of a residential building. It serves as the primary guide for architects, builders, contractors, and interior designers throughout the construction process. Residential plans detail everything from the arrangement of rooms to structural elements and mechanical systems, ensuring that the final home is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Key Components of a Building Plan:
- Site Plan
- Location of the Building: Shows how the house sits on the plot of land, including setbacks, property lines, driveways, and surrounding features such as gardens, roads, or fences.
- Topography: Includes elevation details, slopes, and grading, helping to address drainage, accessibility, and foundation work.
- Landscaping: Initial landscaping concepts like garden areas, trees, outdoor patios, and walkways may be outlined.
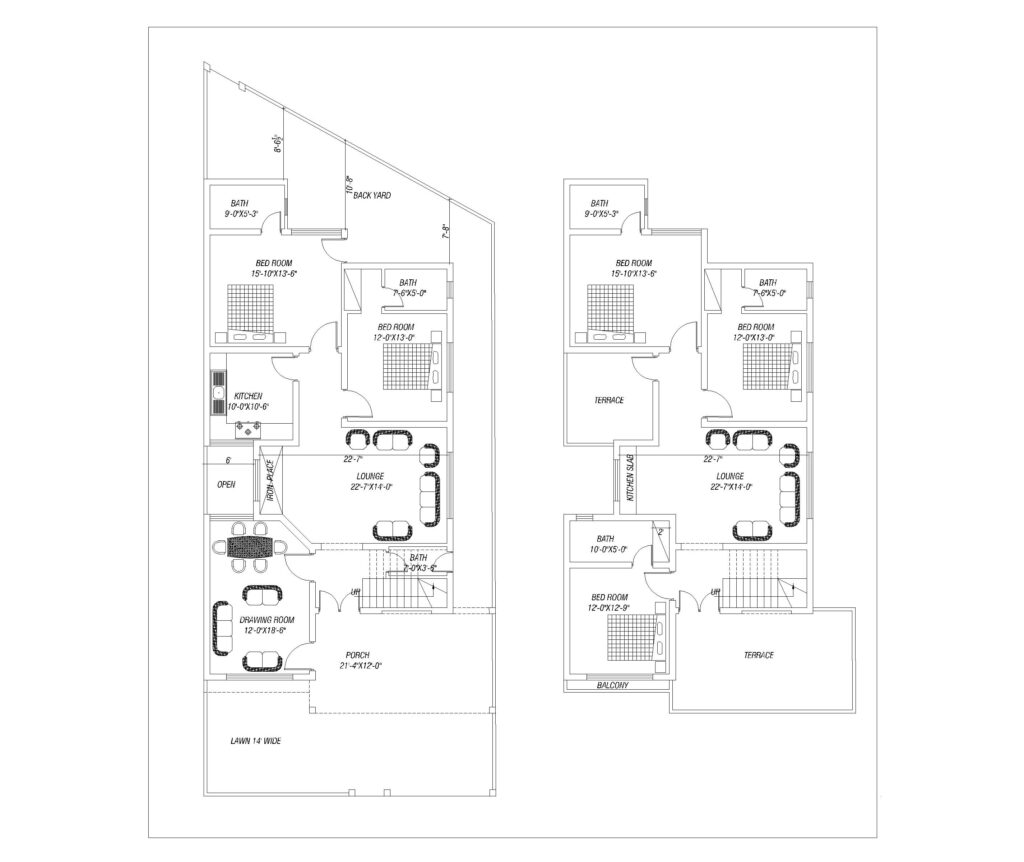
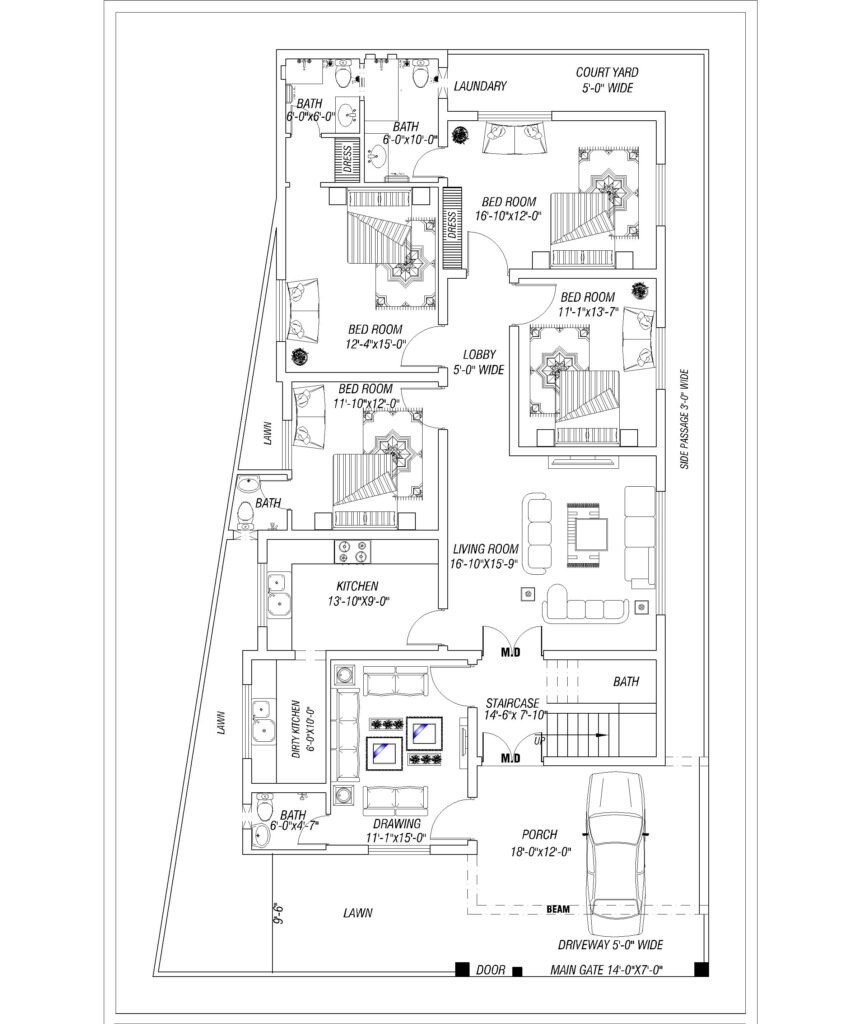
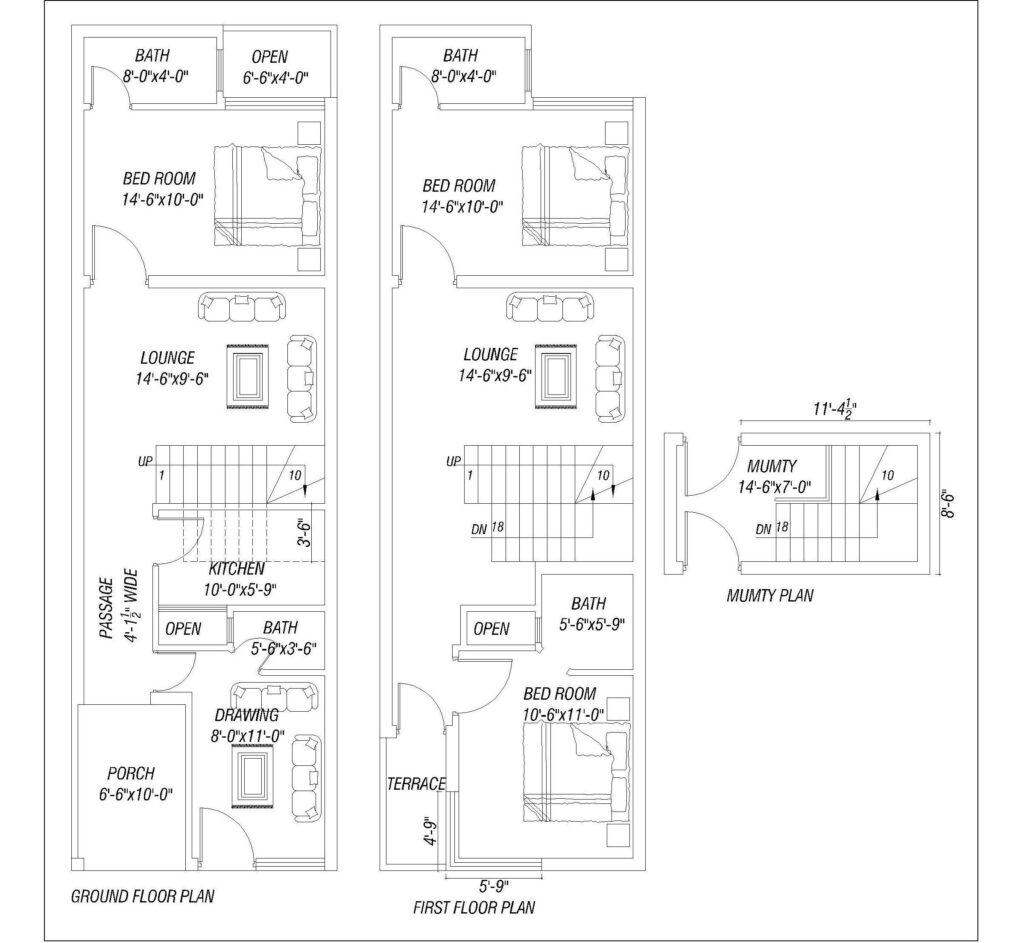
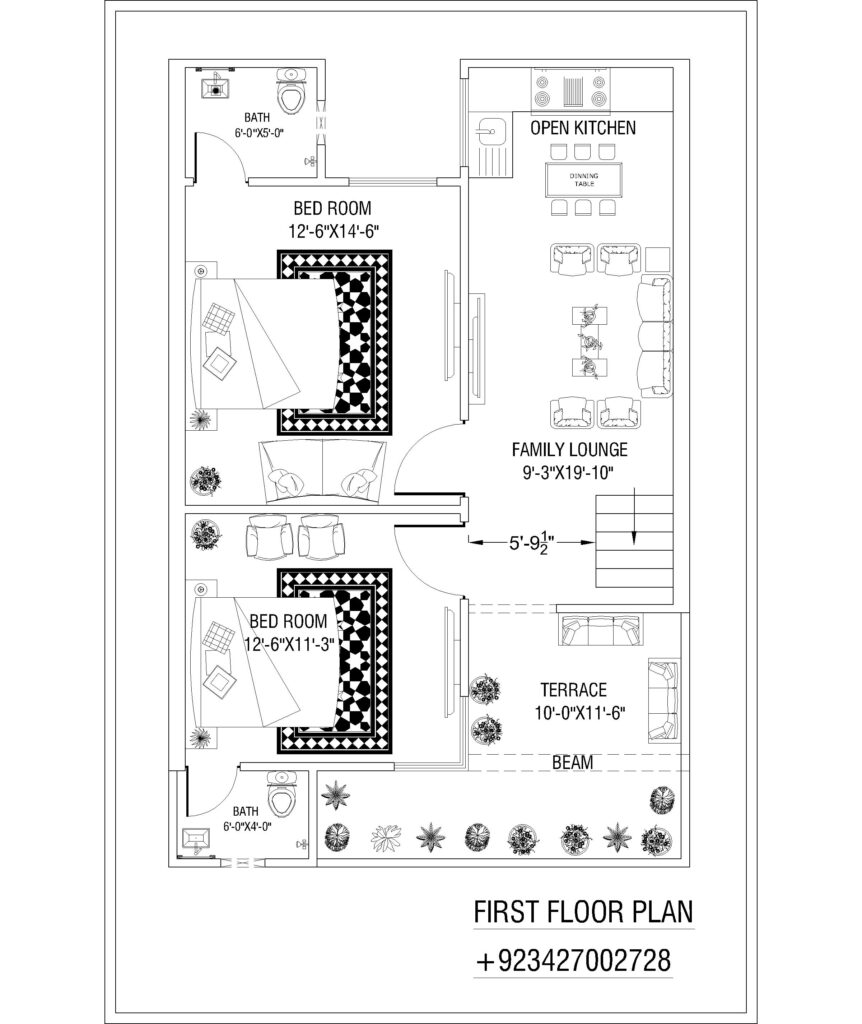
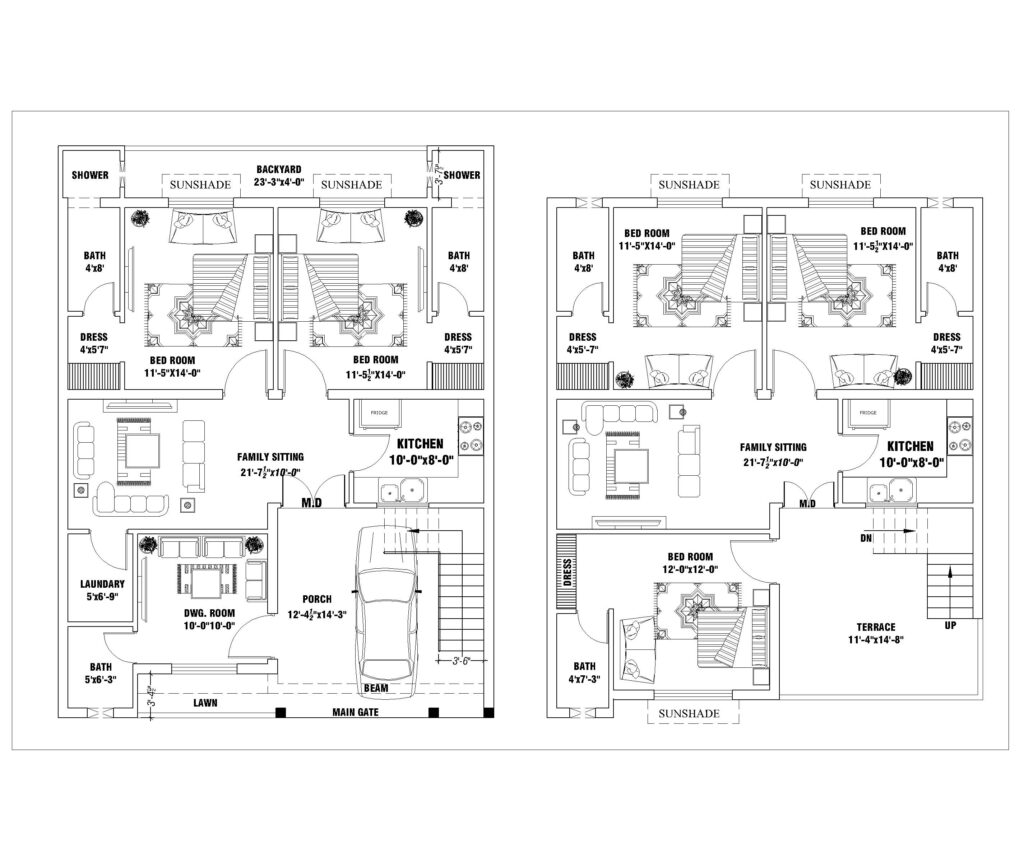
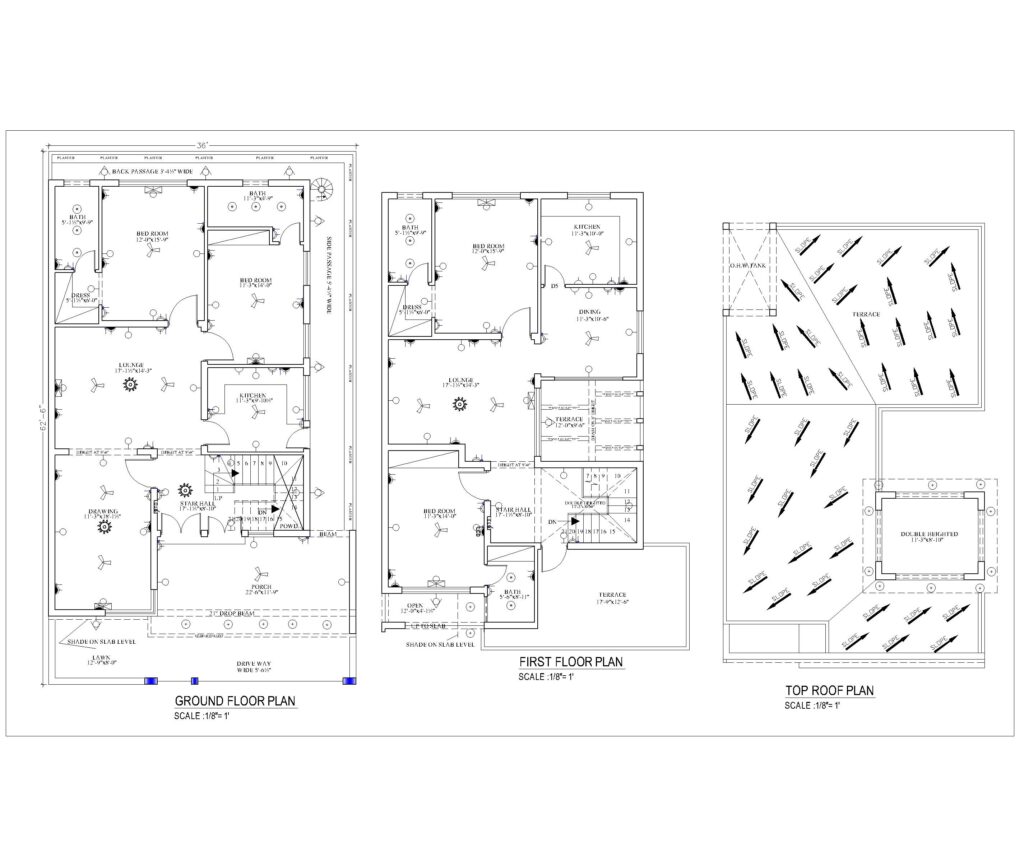
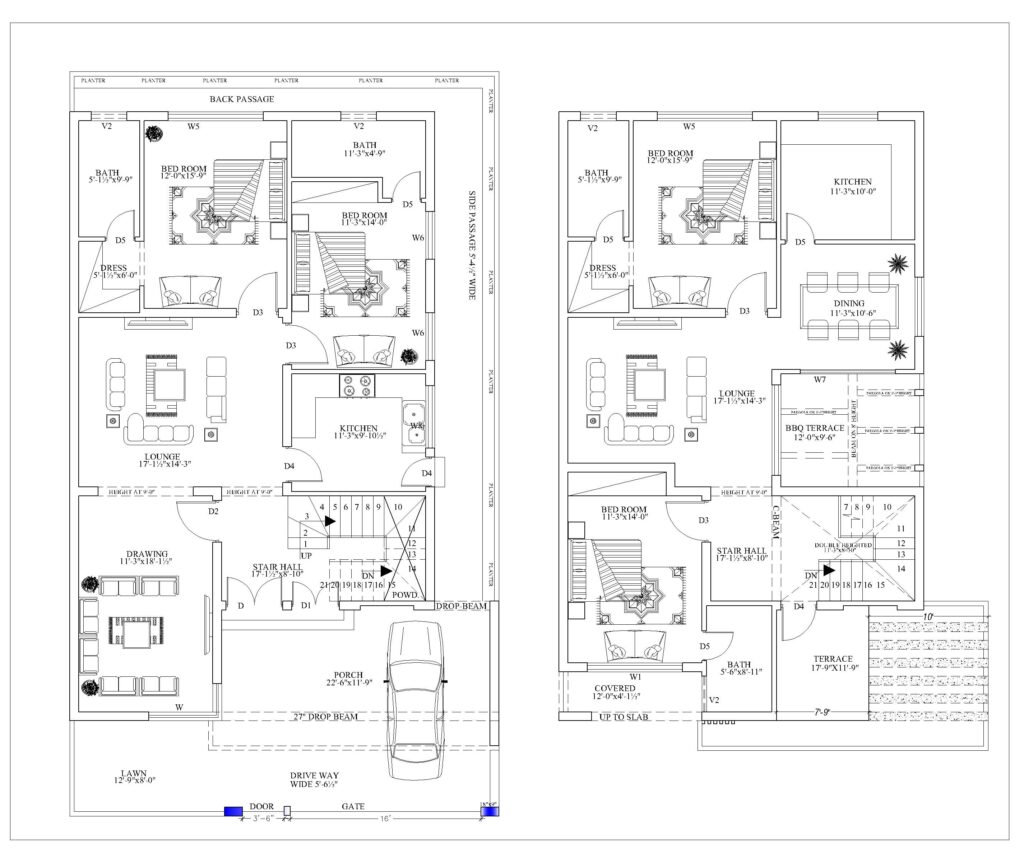
- Floor Plans
- Room Layout: Displays the internal arrangement of rooms, walls, doors, and windows. It helps to visualize the flow of the space, ensuring that the home meets the client’s functional needs.
- Dimensions: Provides the measurements of each room, hallway, and opening.
- Furniture Placement: Often, floor plans also suggest furniture placement to optimize space usage.
- Flow and Circulation: Ensures smooth transition between rooms, considering factors like natural light, ventilation, and access.
- Elevations
- Exterior Views: Shows the exterior design of the house from all sides (front, rear, and sides).
- Architectural Features: Includes roof lines, window designs, door placements, and other exterior details such as trim, siding materials, and finishes.
- Building Height: Elevations help to visualize the height and proportions of the building in relation to the land and other structures.
- Sections and Cross-Sections
- Vertical Slice: A section is like a “cut through” the building that reveals internal spaces and the relationship between floors.
- Ceiling Heights: Details the height of each floor and the placement of structural elements such as beams, columns, and foundations.
- Structural and MEP Systems: Shows the positioning of plumbing, electrical systems, and HVAC ducts within the building.
- Roof Plan
- Roof Shape and Slope: Outlines the design of the roof, including the type of roofing material, the pitch or slope, and any features such as skylights, chimneys, or vents.
- Drainage: Indicates how rainwater will be drained via gutters and downspouts to avoid pooling or flooding.
- Foundation Plan
- Structural Support: Details the layout and type of foundation (slab, crawl space, basement) used to support the structure of the house.
- Footings and Slab Design: Shows how the foundation is connected to the soil and the materials required for proper support.
- Electrical, Plumbing, and Mechanical (MEP) Plans
- Electrical Plan: Illustrates the placement of outlets, switches, lighting, and electrical panels. It shows the wiring layout and how electrical systems connect to the main grid.
- Plumbing Plan: Indicates the placement of pipes, fixtures (e.g., sinks, toilets, bathtubs), and the overall water supply and waste systems.
- HVAC Plan: Displays heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, including ductwork and the location of air conditioning units and heaters.
- Material Specifications and Finishes
- Interior Finishes: Describes the materials used for walls, floors, ceilings, and trim. This includes flooring options (wood, tile, carpet) and wall finishes (paint, wallpaper, paneling).
- Exterior Finishes: Lists materials for exterior walls, roofing, and windows, such as brick, wood, or stucco, ensuring durability and style.
Benefits of a Building Plan:
- Clarity: Provides clear guidelines for builders, reducing the likelihood of mistakes or misunderstandings during construction.
- Efficiency: Ensures the layout optimizes space and functionality while meeting the client’s needs and budget.
- Code Compliance: Ensures that the design adheres to local building codes and regulations, helping the project pass inspections and obtain permits.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Helps create a cohesive, visually pleasing home by considering proportions, design elements, and materials in the overall scheme.
- Long-Term Value: A well-thought-out residential plan contributes to the durability, efficiency, and livability of the home, enhancing its value over time.